Synonymes : Chlorocyperus iria L. Rikli, Cyperus microiria Steud., Cyperus microlepis Baker, Cyperus panicoides Lam.
Common name : Rice flat sedge, umbrella sedge
Common name in Bengali : Barachucha
Common name in Hindi : Morphula, motha
Common name in Urdu : Bhoin






Bangla English Hindi Urdu
Diagnostic characters
Biology
Ecology and distribution
Nuisance
Weed control
Botany
Uses/Remark
References
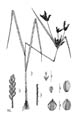
Cyperus iria is an annual herbaceous sedge, tufted and tall, mainly a problem in the rice fields of Asia.This species is distinguished by its yellowish red fibrous roots; its yellowish, usually open inflorescence and by the lowest bract of the flower always being longer than the inflorescence.
In India, the juice of C. iria is used as tonic and to treat stomach aches.
It reproduces from seed; one plant may produce around 3000 to 5000 seeds. The prodigious rate of multiplication of C. iria is due partly to the profusion of seeds and partly to its short life cycle. The seedlings appear soon after rice is sown, the flowers appear in about one month, shed their seeds, and may establish a second generation in the same season.
C. iria is native of tropical Asia and later widespread in subtropical Asia. It is a principal weed in paddy fields throughout the world and is also common in upland fields in many countries (it is reported in 17 crops and in 22 countries).
Concentrated leachates from the roots, shoots and inflorescences of C. iria adversely affect germination, root and shoot growth of rice seedlings.
- Chemical
C. iria is controlled by butachlor and is moderately susceptible to oxadiazon at 075-1.0 kg ha-1 applied after harrowing and sowing of rice. It is also controlled by early post-emergence commercial mixtures of butachlor and propanil, or 2_4-D at 0.5 to 0.8 kg ha-1, MCPA at 0.4 kg ha-1, propanil at 2 kg ha-1 applied 20-30 days after-emergence, or Almix 4 g/ha.
Habit
C. iria is an erect, annual, often amphibious herb up ranging from 20cm to 1 m high.
Roots
Fibrous yellowish red.
Stem
Tufted, 3-angled, green with dull dark reddish at the base.
Leaves
Leaf blades linear-lanceolate, usually all shorter than the culm, 10-30cm long and 3 to 6mm wide; the margins somewhat rough on the upper part; parallel nerves with a distinct, ventrally raised midnerve. Sheaths membranous, enveloping the culm at the base.
Inflorescence
Simple or compound, usually open, up to 20cm long; leaf bracts (involucre) three to five, the lowest one longer than the inflorescence. Spikes elongate, rather dense; spikelets erect-spreading, crowded, 6 to 24-flowered, 5 to 13mm long, 1.5 to 2mm wide, yellow; stigmas three; glume broad-ovate, 1 to 1.5mm long.
Fruit
Small achene, slightly shorter than the glume, the terminal half broader than the base, brown, triangular in cross section, 1 to 1.5mm long.
- Holm L. G., Plucknett D. L., Pancho J. V., Herberger J. P. 1991. The world’s worst weeds. Distribution and Biology. East-West Center by the University Press. Hawaii.
- Galinato M., Moody K., Piggin C. M. 1999. Upland rice weeds of South and Southeast Asia. IRRI. Philippines.
- Radanachaless T., Maxwell J. F. 1994. Weeds of soybean fields in Thailand. Multiple Cropping Center Publications. Thailand.
Top of the page






